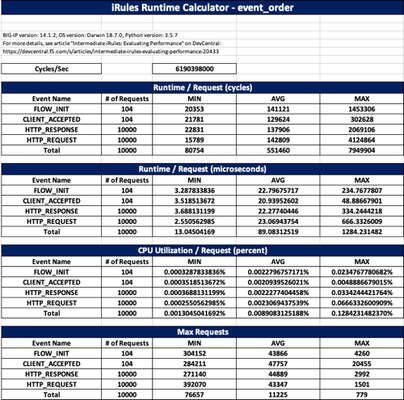
iRules Runtime Calculator Spreadsheet Generator
Problem this snippet solves: This script auto-generates the iRules Runtime Calculator Excel spreadsheet by connecting to BIG-IP, collecting the iRule and its stats, and then using the XlsxWriter module to populate the spreadsheet. Tested on BIG-IP 12.1, 13.1, 14.1, 15.0 with python 3.5, 3.7 from Windows 10 and MacOS Mojave Article details if interested. Screenshots: How to use this snippet: usage: runtime_calc_v2.py [-h] host username rule Tested this on version: 13.0 Download here: GitHub Gist788Views2likes0CommentsRadius External Monitor (Python)
Problem this snippet solves: Note: This script works and is usable however currently the only issue is that for some unknown reason it fails authentication on valid credentials, but since it still gets a valid response from the Radius server it will still mark the pool member as up. This only occurs via a configured monitor using either variable or arguments, running the script via command line with the same arguments works. This python script is an external monitor for radius that checks for any radius response in order to mark a pool member as up. If the connection times out the script does not output any response and as such will result in the member being marked as down. The script strips of routing domain tags and the IPv6 padding of the Node IPs. How to use this snippet: Installation: Import as an External Monitor Program File and name it however you want. Get and copy python modules Six (six py) and Py-Radius (radius py) then copy them to a directory with suitable permissions such as the /config/eav directory. If you're running python 2.6, which you probably will, then the radius module will need to be modified as per Code Mods section in the code below. Monitor Configuration: Set up a monitor with at the very least a valid SECRET, if you're looking to simply test whether the Radius server is alive and responding then the user account does not need to be valid. Valid Environment Variables are as follows: DEBUG = 0, 1, 2 (Default: 0) MOD_PATH = Directory containing the Python modules (Default: /config/eav) SECRET = Radius server secret (Default: NoSecret) USER = User account (Default: radius_monitor) PASSWD = Account Password (Default: NoPassword) Notes: The configured environment variables can overridden using Arguments with TESTME as the first argument followed by the variables you want to override in the same format as above, eg. KEY=Value. This is usedful for troubleshooting and can be used to override the F5 supplied NODE_IP and NODE_PORT variables. Log file location: /var/log/monitors Debug level 2 outputs environment variables, command line arguments and radius module into the log file. Code : #!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # # Filename : radius_mon.py # Author : ATennent # Version : 1.1 # Date : 2018/09/14 # Python ver: 2.6+ # F5 version: 12.0+ # ========== Installation # Import this script via GUI: # System > File Management > External Monitor Program File List > Import... # Name it however you want. # Get, modify and copy the following modules: # ========== Required modules # -- six -- # https://pypi.org/project/six/ # Copy six.py into /config/eav # # -- py-radius -- # https://pypi.org/project/py-radius/ # Copy radius.py into /config/eav # If running python2.6 modify radius.py as per "Code mods -- python.py --" section below # ========== Notes # NB: Any and all outputs from EAV scripts equate to a POSITIVE result by the F5 monitor # so to make the result of the script to be a NEGATIVE result, ie. a DOWN state, we need # to ensure that the script does not output anything when the attempt results in a time out. # ========== Environment Variables # NODE_IP - Supplied by F5 monitor # NODE_PORT - Supplied by F5 monitor # MOD_PATH - Path to location of Python modules six.py and radius.py, default: /config/eav # SECRET - Radius server secret # USER - Username for test account # PASSWD - Password for user account # DEBUG - Enable/Disable Debugging # ========== Additional Environment Variables (supplied at execution) # MON_TMPL_NAME - Monitor Name, eg. '/Common/radius_monitor' # RUN_I - Run file, eg. '/Common/radius_mon.py' # SECURITY_FIPS140_COMPLIANCE - 'true'/'false' # PATH - Colon delimited and not editable. # ARGS_I - Copy of command line Arguments # NODE_NAME - Node Name, eg, '/Common/SNGPCTXWEB01' # MON_INST_LOG_NAME - Pool member's monitor log, eg. '/var/log/monitors/Common_radius_monitor-Common_MyNode-1812.log' # SECURITY_COMMONCRITERIA - 'true'/'false' # ========== Code mods -- python.py -- # Dictionary comprehension fixes: # https://stackoverflow.com/questions/1747817/create-a-dictionary-with-list-comprehension-in-python#1747827 # LINE:193; replace with #ATTR_NAMES = dict((v.lower(), k) for (k, v) in ATTRS.items()) # # LINE:100; replace with #CODE_NAMES = dict((v.lower(), k) for (k, v) in CODES.items()) # # Logger.NullHandler fix: # https://stackoverflow.com/questions/33175763/how-to-use-logging-nullhandler-in-python-2-6#34939479 # LINE:64-65; replace with #LOGGER = logging.getLogger(__name__) #try: # Python 2.7+ # LOGGER.addHandler(logging.NullHandler()) #except AttributeError: # class NullHandler(logging.Handler): # def emit(self, record): # pass # LOGGER.addHandler(NullHandler()) # ========== Imports/Modules from sys import path from sys import argv from sys import stdout from os import environ import logging.handlers import re if environ.get('MOD_PATH'): path.append(environ.get('MOD_PATH')) else: path.append('/config/eav') import radius # ========== Dictionary Defaults opts_dict = {'NODE_IP': '', 'NODE_PORT': '', 'SECRET': 'NoSecret', 'USER': 'radius_monitor', 'PASSWD': 'NoPassword', 'DEBUG': '0', } # ========== TEST w/ command line try: if argv[3] == 'TESTME': environ['NODE_IP'] = argv[1] environ['NODE_PORT'] = argv[2] for cmd_opt in argv[3:]: if 'DEBUG' in cmd_opt: environ['DEBUG'] = cmd_opt.split('=')[1] elif 'SECRET' in cmd_opt: environ['SECRET'] = cmd_opt.split('=')[1] elif 'USER' in cmd_opt: environ['USER'] = cmd_opt.split('=')[1] elif 'PASSWD' in cmd_opt: environ['PASSWD'] = cmd_opt.split('=')[1] else: continue except: pass # ========== Logging Config try: if int(environ.get('DEBUG')) == 0: log_file = '/dev/null' elif int(environ.get('DEBUG')) <=2: log_file = environ.get('MON_INST_LOG_NAME') else: log_file = '/dev/null' except: # DEBUG not supplied as ENV variable environ['DEBUG'] = opts_dict['DEBUG'] log_file = '/dev/null' if int(environ.get('DEBUG')) == 2: logging.basicConfig( filename=log_file, level=logging.DEBUG, format='%(asctime)s %(name)s:%(levelname)s %(message)s') else: logging.basicConfig( filename=log_file, level=logging.INFO, format='%(asctime)s %(name)s:%(levelname)s %(message)s') log = logging.getLogger('radius_mon') syslog_handler = logging.handlers.SysLogHandler(address='/dev/log', facility=0) log.addHandler(syslog_handler) if int(environ.get('DEBUG')) == 0: log.setLevel(logging.INFO) opts_dict['DEBUG'] = environ.get('DEBUG') elif int(environ.get('DEBUG')) == 1: log.setLevel(logging.DEBUG) opts_dict['DEBUG'] = environ.get('DEBUG') elif int(environ.get('DEBUG')) == 2: log.setLevel(logging.DEBUG) opts_dict['DEBUG'] = environ.get('DEBUG') log.debug('VERBOSE Debug Enabled, CMD line and ENV variables will be dumped to file.') else: log.error('Bad DEBUG value!') # ========== CMD Line and ENV Dump if int(opts_dict['DEBUG']) == 2: log.debug('=========== CMD ARGS') log.debug(argv[0:]) log.debug('=========== ENV VARS') log.debug(environ) # ========== Update Dictionary if environ.get('NODE_IP'): opts_dict['NODE_IP'] = environ.get('NODE_IP') log.debug('Set NODE_IP, %s', opts_dict['NODE_IP']) else: log.error('NODE_IP not supplied as ENV variable') log.error('Exiting..') exit(0) if environ.get('NODE_PORT'): opts_dict['NODE_PORT'] = environ.get('NODE_PORT') log.debug('Set NODE_PORT, %s', opts_dict['NODE_PORT']) else: log.error('NODE_PORT not supplied as ENV variable') log.error('Exiting..') exit(0) if environ.get('SECRET'): opts_dict['SECRET'] = environ.get('SECRET') log.debug('Set SECRET, %s', opts_dict['SECRET']) else: log.debug('SECRET not supplied as ENV variable') if environ.get('USER'): opts_dict['USER'] = environ.get('USER') log.debug('Set USER, %s', opts_dict['USER']) else: log.debug('USER not supplied as ENV variable') if environ.get('PASSWD'): opts_dict['PASSWD'] = environ.get('PASSWD') log.debug('Set PASSWD, %s', opts_dict['PASSWD']) else: log.debug('PASSWD not supplied as ENV variable') # ========== Clean up NODE_IP for IPv4 if '::ffff:' in opts_dict['NODE_IP']: opts_dict['NODE_IP'] = re.sub(r'::ffff:','', opts_dict['NODE_IP']) log.debug('Stripped IPv6 notation from IPv4 address') # ========== Strip routing domain from NODE_IP if '%' in opts_dict['NODE_IP']: opts_dict['NODE_IP'] = re.sub(r'%\d{1,4}$', '', opts_dict['NODE_IP']) log.debug('Stripped routing domain from IP address') # ========== Dictionary debug if int(opts_dict['DEBUG']) == 2: log.debug('----- KEY, VALUE pairs:') for key in opts_dict.keys(): log.debug('%s, %s', key, opts_dict[key]) log.debug('-----') # ========== Main r = radius.Radius(opts_dict['SECRET'], host=opts_dict['NODE_IP'], port=int(opts_dict['NODE_PORT'])) try: if r.authenticate(opts_dict['USER'], opts_dict['PASSWD']): log.debug('Service UP, Authentication attempt Successful') stdout.write('UP') else: log.debug('Service UP, Authentication attempt Failure') stdout.write('UP') except radius.ChallengeResponse: log.debug('Service UP, Authentication attempt Challenge Response') stdout.write('UP') except (radius.NoResponse, radius.SocketError): # This includes bad SECRET keys, the radius RFC states that Invalid responses from the radius # server are to be silently dropped which, from a client perspective, will result ina timeout. # This cannot be changed without modifying radius.py to instead raise an Exception. log.debug('No Response from %s:%s', opts_dict['NODE_IP'], int(opts_dict['NODE_PORT'])) exit(0) except Exception as msg: log.error('Exception due to %s, marking as DOWN', msg) exit(0) Tested this on version: 12.0985Views1like0CommentsTACACS+ External Monitor (Python)
Problem this snippet solves: This script is an external monitor for TACACS+ that simulates a TACACS+ client authenticating a test user, and marks the status of a pool member as up if the authentication is successful. If the connection is down/times out, or the authentication fails due to invalid account settings, the script marks the pool member status as down. This is heavily inspired by the Radius External Monitor (Python) by AlanTen. How to use this snippet: Prerequisite This script uses the TACACS+ Python client by Ansible (tested on version 2.6). Create the directory /config/eav/tacacs_plus on BIG-IP Copy all contents from tacacs_plus package into /config/eav/tacacs_plus. You may also need to download six.py from https://raw.githubusercontent.com/benjaminp/six/master/six.py and place it in /config/eav/tacacs_plus. You will need to have a test account provisioned on the TACACS+ server for the script to perform authentication. Installation On BIG-IP, import the code snippet below as an External Monitor Program File. Monitor Configuration Set up an External monitor with the imported file, and configure it with the following environment variables: KEY: TACACS+serversecret USER: Usernamefortestaccount PASSWORD: Passwordfortestaccount MOD_PATH: PathtolocationofPythonpackagetacacs_plus,default:/config/eav TIMEOUT: DurationtowaitforconnectivitytoTACACSservertobeestablished,default:3 Troubleshooting SSH to BIG-IP and run the script locally $ cd /config/filestore/files_d/Common_d/external_monitor_d/ # Get name of uploaded file, e.g.: $ ls -la ... -rwxr-xr-x. 1 tomcat tomcat 1883 2021-09-17 04:05 :Common:tacacs-monitor_39568_7 # Run the script with the corresponding variables $ KEY=<my_tacacs_key> USER=<testuser> PASSWORD=<supersecure> python <external program file, e.g.:Common:tacacs-monitor_39568_7> <TACACS+ server IP> <TACACS+ server port> Code : #!/usr/bin/env python # # Filename : tacacs_plus_mon.py # Author : Leon Seng # Version : 1.2 # Date : 2021/09/21 # Python ver: 2.6+ # F5 version: 12.1+ # # ========== Installation # Import this script via GUI: # System > File Management > External Monitor Program File List > Import... # Name it however you want. # Get, modify and copy the following modules: # ========== Required modules # -- six -- # https://pypi.org/project/six/ # Copy six.py into /config/eav # # -- tacacs_plus -- # https://pypi.org/project/tacacs_plus/ | https://github.com/ansible/tacacs_plus # Copy tacacs_plus directory into /config/eav # ========== Environment Variables # NODE_IP - Supplied by F5 monitor as first argument # NODE_PORT - Supplied by F5 monitor as second argument # KEY - TACACS+ server secret # USER - Username for test account # PASSWORD - Password for test account # MOD_PATH - Path to location of Python package tacacs_plus, default: /config/eav # TIMEOUT - Duration to wait for connectivity to TACACS server to be established, default: 3 import os import socket import sys if os.environ.get('MOD_PATH'): sys.path.append(os.environ.get('MOD_PATH')) else: sys.path.append('/config/eav') # https://github.com/ansible/tacacs_plus from tacacs_plus.client import TACACSClient node_ip = sys.argv[1] node_port = int(sys.argv[2]) key = os.environ.get("KEY") user = os.environ.get("USER") password = os.environ.get("PASSWORD") timeout = int(os.environ.get("TIMEOUT", 3)) # Determine if node IP is IPv4 or IPv6 family = None try: socket.inet_pton(socket.AF_INET, node_ip) family = socket.AF_INET except socket.error: # not a valid address try: socket.inet_pton(socket.AF_INET6, node_ip) family = socket.AF_INET6 except socket.error: sys.exit(1) # Authenticate against TACACS server client = TACACSClient(node_ip, node_port, key, timeout=timeout, family=family) try: auth = client.authenticate(user, password) if auth.valid: print "up" except socket.error: # EAV script marks node as DOWN when no output is present pass Tested this on version: 12.11KViews1like0CommentsiRule stats formatter
Problem this snippet solves: When you have a load of iRule stats in text format from your F5 device and need to get them into a nicer format. The following Python 3 script takes in a text file in the following format: ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Ltm::Rule Event: /web_testing/test_environment_rule:HTTP_RESPONSE ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Priority 12 Executions Total 31686860 Failures 0 Aborts 0 CPU Cycles on Executing Average 404058 Maximum 10703959 Minimum 264201 (raw) ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Ltm::Rule Event: /web_testing/test_environment_rule:HTTP_REQUEST ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Priority 899 Executions Total 31686860 Failures 0 Aborts 0 CPU Cycles on Executing Average 404058 Maximum 10703959 Minimum 264201 Put through the following python script to output a CSV file for further data manipulation. How to use this snippet: Python3 script, to use run the following (can also add in '--o' to define an output file, if not will replace the file extension '.txt' with '.csv' by default): python statformating.py --i my_irule_stats.txt output will be something like Openning 'my_irule_stats.txt' Saving output csv to 'my_irule_stats.csv' Usage/help output: usage: statformating.py [-h] [--i INPUT] [--o OUTPUT] optional arguments: -h, --help show this help message and exit --i INPUT iRule Stats File input file name --o OUTPUT iRule Stats File output csv file name Code : import re import os import argparse def iruleStatsFormat(inputFile, outputFile): print('Openning \'{}\''.format(inputFile)) iruleStats = open(inputFile, 'rt').read() iruleStats = re.sub(r'[ ]{2,}', ' ', iruleStats) iruleStats = re.sub(r'\n\s\(raw\)\s{1,}', '', iruleStats) iruleStats = re.sub(r'[-]{2,}\n', '', iruleStats) iruleStats = re.sub(r'\n ', r'\n', iruleStats) iruleStats = re.sub(r'CPU Cycles on Executing\n', '', iruleStats) iruleStats = re.sub(r'Executions \n', '', iruleStats) iruleStats = re.sub(r'\nPriority (\d{1,})\nTotal (\d{1,})\nFailures (\d{1,})\nAborts (\d{1,})\nAverage (\d{1,})\nMaximum (\d{1,})\nMinimum (\d{1,})', r'\t\1\t\2\t\3\t\4\t\5\t\6\t\7', iruleStats) iruleStats = re.sub(r'Ltm::Rule Event: /(.*?)/(.*?):(.*?\t)', r'\1\t\2\t\3', iruleStats) iruleStats = re.sub(r'Ltm::Rule Event: (.*?):(.*?\t)', r'Common\t\1\t\2', iruleStats) iruleStats = re.sub(r'\n{2,}', r'\n', iruleStats) iruleStats = re.sub(r'\t', r',', iruleStats) print('Saving output csv to \'{}\''.format(outputFile)) with open(outputFile, 'wt') as f: print(iruleStats, file=f) if __name__=='__main__': parser = argparse.ArgumentParser() parser.add_argument("--i", dest='input', help="iRule Stats File input file name", type=str) parser.add_argument("--o", dest='output', help="iRule Stats File output csv file name", type=str, default="") args = parser.parse_args() if args.input and os.path.isfile(args.input): if not args.output: args.output = args.input[:-3] + 'csv' iruleStatsFormat(args.input, args.output) else: parser.print_help()265Views1like0Comments