How To Run Ollama On F5 AppStack With An NVIDIA GPU In AWS
If you're just getting started with AI, you'll want to watch this one, as Michael Coleman shows Aubrey King, from DevCentral, how to run Ollama on F5 AppStack on an AWS instance with an NVIDIA Tesla T4 GPU. You'll get to see the install, what it looks like when a WAF finds a suspicious conversation and even a quick peek at how Mistral handles a challenge differently than Gemma. 86Views2likes0Comments
86Views2likes0CommentsParsing F5 BIG-IP LTM DNS profile statistics and extracting values with Python
Introduction Hello there! Arvin here from the F5 SIRT. A little while ago, I published F5BIG-IP Advanced Firewall Manager (AFM) DNS NXDOMAIN Query Attack Type Walkthroughpart one and two, where I went through the process of reviewing BIG-IP LTM DNS profile statistics and used it to set BIG-IP AFM DNS NXDOMAIN Query attack type detection and mitigation thresholds with the goal of mitigating DNS NXDOMAIN Floods. In this article, I continue to look atBIG-IP LTM DNS profile statistics, find ways of parsing it and to extract specific values of interest through Python. Python for Network Engineers Python has emerged as a go-to language for network engineers, providing a powerful and accessible toolset for managing and automating network tasks. Known for its simplicity and readability, Python enables network engineers to script routine operations, automate repetitive tasks, and interact with network devices through APIs. With extensive libraries and frameworks tailored to networking, Python empowers engineers to streamline configurations, troubleshoot issues, and enhance network efficiency. Its versatility makes it an invaluable asset for network automation, allowing engineers to adapt to evolving network requirements and efficiently manage complex infrastructures. Whether you're retrieving data, configuring devices, or optimizing network performance, Python simplifies the process for network engineers, making it an essential skill in the modern networking landscape. The Tools ChatGPT3.5 The "Python for Network Engineers" intro came from ChatGPT3.5 [:)]. Throughout this article, the python coding "bumps" avoidance and approaches came from ChatGPT3.5. Instead of googling, I asked ChatGPT "a lot" so I could get the python scripts to get the output I wanted. https://chat.openai.com/ Visual Studio Code UsingVisual Studio Code (VSCode) to build the scripts was very helpful, especially the tooltip / hints which tells me and help make sense of the available options for the modules used and describing the python data structures. Python 3.10 (From ChatGPT)Python 3.10, the latest version of the Python programming language, brings forth new features and optimizations that enhance the language's power and simplicity. With Python's commitment to readability and ease of use, version 3.10 introduces structural pattern matching, allowing developers to express complex logic more concisely. Other improvements include precise types, performance enhancements, and updates to syntax for cleaner code. Python 3.10 continues to be a versatile and accessible language, serving diverse needs from web development to data science and automation. Its vibrant community and extensive ecosystem of libraries make Python 3.10 a top choice for developers seeking both efficiency and clarity in their code. Python Script - extract DNS A requests value from LTM DNS profile statistics iControl REST output This python script will extract DNS A requests value from LTM DNS profile statistics iControl REST output. Python has many modules that can be used to simplify tasks. iControl REST output is in json format, so as expected, I used the json module. I wanted to format the output data in csv format so the extracted data can later be used in other tools that consume csv formatted data, thus, I used the csv module. I also used the os, time/datetime and tabulate modules for working with the filesystem (I used a Windows machine to run Python and VSCode) to write csv files. Create variables with date and time information that will be used in formatting the csv file name, keep track of the "A record requests" value at script execution, and present a tabulated output of the captured time and data when the script is executed. I also used BIGREST module to query/retrieve the "show ltm dns profile <DNS profile> statistics" instead of getting the output from iControl REST request sent through other methods. https://bigrest.readthedocs.io/introduction.html https://bigrest.readthedocs.io/bigip_show.html Here is the sample script output Here is the sample CSV-formatted data in a csv file with timestamp of the script run I created a github repository for the Python script and its sample script output and csv data see https://github.com/arvfopa/scripts/tree/main https://github.com/arvfopa/scripts/blob/main/extractAreq- Python Script "extractAreq" https://github.com/arvfopa/scripts/blob/main/extractAreq_output- "extractAreq" output Bumps along the way BIGREST module I initially encountered an error 'certificate verify failed: self signed certificate' when provided only the IP address and credentials used in the BIGIP class of the bigrest.bigip python module raise SSLError(e, request=request) requests.exceptions.SSLError: HTTPSConnectionPool(host='IP address', port=443): Max retries exceeded with url: /mgmt/shared/echo-query (Caused by SSLError(SSLCertVerificationError(1, '[SSL: CERTIFICATE_VERIFY_FAILED] certificate verify failed: self signed certificate (_ssl.c:1007)'))) This is fixed by setting "session_verify" argument of the BIGIP class to "false" to disables SSL certificate validation device = BIGIP("<IP address>", "<username>", "<password>" , session_verify=False) https://bigrest.readthedocs.io/utils.html I also received this error "TypeError: Object of type RESTObject is not JSON serializable" raise TypeError(f'Object of type {o.__class__.__name__} ' TypeError: Object of type RESTObject is not JSON serializable I reread the BIGREST documentation and found that the output is a python dictionary and can is printed in json format.I rechecked the script and removed the json related syntax and module, and the script runs fine and still gets the same output. I updated the script on github with the simplified changes. https://bigrest.readthedocs.io/restobject.html Here's a sample of the RESTObject properties dictionary values. Plenty of data can be extracted. Example, "clientside.pktsIn" value, a virtual server statistic, can be observed and should detection and mitigation thresholds for AFM, say, UDP protocol DoS attack type, need to be set. This value can be monitored over time to understand how many packets a virtual server receives. ============== {'clientside.bitsIn': {'value': 0}, 'clientside.bitsOut': {'value': 0}, 'clientside.curConns': {'value': 0}, 'clientside.evictedConns': {'value': 0}, 'clientside.maxConns': {'value': 0}, 'clientside.pktsIn': {'value': 0}, 'clientside.pktsOut': {'value': 0}, 'clientside.slowKilled': {'value': 0}, 'clientside.totConns': {'value': 0}, 'cmpEnableMode': {'description': 'all-cpus'}, 'cmpEnabled': {'description': 'enabled'}, 'csMaxConnDur': {'value': 0}, 'csMeanConnDur': {'value': 0}, 'csMinConnDur': {'value': 0}, 'destination': {'description': '10.73.125.137:53'}, 'ephemeral.bitsIn': {'value': 0}, 'ephemeral.bitsOut': {'value': 0}, 'ephemeral.curConns': {'value': 0}, 'ephemeral.evictedConns': {'value': 0}, ============== CSV filename issue I encountered thiserror,"OSError: [Errno 22] Invalid argument: 'dns_stats_2023-12-07_18:01:11.csv". This is related to writing of the output csv file. I asked ChatGPT what this was about andwas providedwith thisanswer. ======================= The error you're encountering, "[Errno 22] Invalid argument," typically suggests an issue with the filename or file path. In this case, it seems to be related to the colon (':') character in the filename. In some operating systems (like Windows), certain characters are not allowed in filenames, and ":" is one of them. Since you're including a timestamp in the filename, it's common to replace such characters with alternatives. You can modify the timestamp format to use underscores or hyphens instead of colons. ==================== The timestamp variable in the script stores the value of the formatted timestamp that will be used in the filename. It initially used a colon (:) as the hour/min/sec separator. It was changed to dash (-) so it would not encounter this error. timestamp = datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S") Checking the file csv file if it exists The function "write_to_csv" writes the time of collection (formatted_date) andextracted value of DNS A requests count (AReqsvalue). It is called every 10 seconds [time.sleep(10)] for a minute [end_time = time.time() + 60] and writes the output to a file in csv format. The "tabulate" function formats the output of the script. Getting the arrangement of the execution wrong would result in unexpected output. The "file_exists" check to write the "headers" was added to make sure that the "headers" are only written once. "write_to_csv" function ======================== def write_to_csv(formatted_date, AReqsvalue): current_datetime = datetime.now() formatted_date = current_datetime.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S") csv_filename = f"dns_stats_{timestamp}.csv" headers = ["Date", "DNS A requests"] stats = [[formatted_date, AReqsvalue]] file_exists = os.path.exists(csv_filename) print(tabulate(stats, headers, tablefmt="fancy_grid")) with open(csv_filename, mode='a', newline='') as file: writer = csv.writer(file) if not file_exists: writer.writerow(headers) writer.writerows(stats) end_time = time.time() + 60 while time.time() < end_time: write_to_csv(formatted_date, AReqsvalue) time.sleep(10) ========================== Using ChatGPT In building this script, I usedChatGPT "a lot" and it helped to provide make more sense of the module options, errors and sample scripts. It has been a helpful tool. It tracks your conversation/questions to it and kind of understands the context/topic. "ChatGPT can make mistakes. Consider checking important information." is written at the bottom of the page. The data I used in this article are data from a lab environment.That said, when using public AI/ML systems, we should ensure we do not send any sensitive, proprietary information. Organizations have rolled out their own privacy policies when using AI/ML systems, be sure to follow your own organization's policies. Conclusion Using python to parse and extract values of interest from LTM profile statistics offers flexibility and hopefully simplifying observing and recording these data for further use. In particular, setting values for BIG-IP AFM DoS Detection and Mitigation thresholds will be easier if such data has been observed as it, in my opinion, is the "pulse" of the traffic the BIG-IP processes. As noted in the sample json data output, we can see many statistics that can be reviewed and observed to make configuration changes relevant, for example, mitigating a connection spike by setting a VS connection/rate limit. We can look at the "Conns" values and use the observed values to set a connection limit. Example: 'clientside.curConns': {'value': 0}, 'clientside.evictedConns': {'value': 0}, 'clientside.maxConns': {'value': 0}, 'clientside.totConns':{'value': 0} That's it for now. I hope this article has been educational. The F5 SIRT createssecurity-related content posted here in DevCentral, sharing the team's security mindset and knowledge. Feel free to view the articles that are tagged withthe following: F5 SIRT series-F5SIRT-this-week-in-security TWIS550Views2likes0CommentsBYOVD, Rust Windows core, RSA Conference 2023 , more-April 22-28th- F5 SIRT-This Week in Security
F5 SIRT This Week in Security BYOVD, Rust in Windows core and RSA Conference 2023 and more April 22nd-28th 2023 Editor's introduction Arvin is your editor for F5 SIRT's This Week in Security covering 22nd-28th of April. Here's a summary of the security news I gathered for this edition. BYOVD - bring-your-own-vulnerable-driver (BYOVD) attack abuses legitimate driver to disable endpoint detection and response software. AuKill, a detection evasion utility, dupes a target system in trusting an outdated MS process explorer and disable EDR processes. AuKill brought the bad driver with it to exploit as it infiltrated the victims' networks. MS has a list of bad and banned drivers that can be implemented with Windows Defender Application Control policy to counter this attack. Apache Superset, a modern data exploration and visualization platform, shipped with an insecure default configuration that could be exploited to login and take over the data visualization application, steal data, and execute malicious code. Documented as CVE-2023-27524, a new update titled "fix: refuse to start with default secret on non debug envs" will prevent superset to start as researchers highlighted, after a year of reporting to Apache security team, users have not addressed the issue, thus, a harsher measure. Some good news, a memory safe language, Rust, will be at the core of the Windows OS. This hopefully means, less memory safety bugs before the code lands in the hands of users which is about 70 percent of the CVE-listed security vulnerabilities patched by the Windows since 2006. In crypto crime news and some win for the defenders, US DoJ and the treasury dept are pursuing 3 men accused of wide-ranging and complex conspiracies, providing support to the notorious Lazarus Group, laundering stolen and illicit cryptocurrency that the North Korean regime used to finance its massive weapons programs. The DPRK is tied to the Lazarus group - a North Korean state-sponsored cyber threat group. Google obtained a court order to shut down domains used to distribute CryptBot after suing the distributors of the info-stealing malware. Litigation was filed against several of CryptBot's major distributors whom are believed to be based in Pakistan and operate a worldwide criminal enterprise. AI-powered attacks - Generative AI, the result of decades of research into neural networking and Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), is widely seen as the next candidate on this list. The idea that AI is a big deal is nothing new and the generative AI that has made headlines is only one subsector of AI development. Chatbots such as OpenAI's ChatGPT and Google's Bard has fired a jolt of destabilizing energy into computing as a whole, and cybersecurity as a discipline. We know its coming and probably have already arrived, complex automated attacks can cost so much to the defenders, keeping them/us busy defending. At attack surfaces where F5 technologies are present, particularly in protecting web applications, F5 has made use of AI and ML in our defensive capabilities. F5 ASM/Adv WAF have used ML in its learning and policy building feature since the early versions of 14.1, and with F5 Distributed Cloud API Security in its automatic API discovery, threat detection, and schema enforcement and F5 Distributed Cloud WAAP - the web application and API WAF, utilizes AI and ML on unique malicious user detection and mitigation capabilities that create a per-user threat score based on behavioral analysis that determines intent. The RSA Conference 2023 in the bay area had just concluded and it had many great talks and learnings. Thoughts from various vendors shared views on the current security landscape, challenges and the future, particularly, the automated/AI class of attacks. Defenders have tools and secure practices - SOCs, the devsecops, and well thought and critical incident response - to hopefully, prevent cyber security incidents and impact to business. on a lighter note, F5 DevCentral folks were also in RSA Conference 2023 and have a nice wrap up video. I hope this summary is informative. Thanks for reading and see you on the next one. How fiends abuse an out-of-date Microsoft Windows driver to infect victims https://www.theregister.com/2023/04/24/microsoft_windows_driver_aukill_ransomware Ransomware spreaders have built a handy tool that abuses an out-of-date Microsoft Windows driver to disable security defenses before dropping malware into the targeted systems. This detection evasion utility, which Sophos X-Ops researchers are calling AuKill, is the latest example in a growing trend where miscreants either abuse a legitimate driver to disable, silence or otherwise get past endpoint detection and response (EDR) software on the systems – the so-called bring-your-own-vulnerable-driver (BYOVD) attack – or work to get a malicious driver that does the same digitally signed by a trusted entity and injected onto a victim's computer. Either way, the victim's PC is duped into trusting a privileged driver, granting an intruder low-level rights and access, which gives them the ability to side step any protections and deploy their malware. And to be clear, AuKill takes the BYOVD approach: it brings onto the PC a vulnerable Microsoft driver to exploit. "Last year, the security community reported about multiple incidents where drivers have been weaponized for malicious purposes," Andreas Klopsch, a threat researcher at Sophos, wrote in a technical report this month."The discovery of such a tool confirms our assumption that adversaries continue to weaponize drivers, and we expect even more development in this area the upcoming months." "The AuKill tool requires administrative privileges to work, but it cannot give the attacker those privileges," writes Klopsch at Sohpos. "The threat actors using AuKill took advantage of existing privileges during the attacks, when they gained them through other means." To defend against this, ensure your environment can detect and block bad and banned drivers from being installed and/or run. Microsoft has some notes about that here. https://news.sophos.com/en-us/2023/04/19/aukill-edr-killer-malware-abuses-process-explorer-driver/ https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/security/threat-protection/windows-defender-application-control/microsoft-recommended-driver-block-rules Apache Superset: A story of insecure default keys, thousands of vulnerable systems, few paying attention https://www.theregister.com/2023/04/25/apache_superset_cve Apache Superset until earlier this year shipped with an insecure default configuration that miscreants could exploit to login and take over the data visualization application, steal data, and execute malicious code. The open source application, based on Python's Flask framework, defaulted to a publicly known secret key: SECRET_KEY = '\2\1thisismyscretkey\1\2\e\y\y\h' According to Sunkavally, about two-thirds of those using the software failed to generate a new key when setting up Superset: as of October 11, 2021, the application had almost 3,000 instances exposed to the internet, about 2,000 of which relied on the default secret key. The Apache security team responded the following day and by January 11, 2022, made some changes, which established a new default secret key: "CHANGE_ME_TO_A_COMPLEX_RANDOM_SECRET" Microsoft is busy rewriting core Windows code in memory-safe Rust https://www.theregister.com/2023/04/27/microsoft_windows_rust Microsoft is rewriting core Windows libraries in the Rust programming language, and the more memory-safe code is already reaching developers. David "dwizzle" Weston, director of OS security for Windows, announced the arrival of Rust in the operating system's kernel at BlueHat IL 2023 in Tel Aviv, Israel, last month."You will actually have Windows booting with Rust in the kernel in probably the next several weeks or months, which is really cool," he said. "The basic goal here was to convert some of these internal C++ data types into their Rust equivalents." Microsoft showed interest in Rust several years ago as a way to catch and squash memory safety bugs before the code lands in the hands of users; these kinds of bugs were at the heart of about 70 percent of the CVE-listed security vulnerabilities patched by the Windows maker in its own products since 2006. The Rust toolchain strives to prevent code from being built and shipped that is exploitable, which in an ideal world reduces opportunities for miscreants to attack weaknesses in software. Simply put, Rust is focused on memory safety and similar protections, which cuts down on the number of bad bugs in the resulting code. Rivals like Google have already publicly declared their affinity for Rust. Rust "Hello World" -https://doc.rust-lang.org/rust-by-example/hello.html DoJ, Treasury accuses 3 men of laundering crypto for North Korea https://www.theregister.com/2023/04/26/doj_treasury_sanctions_north_korea If the DPRK is named, you know it somehow involves Lazarus Group The US government is aggressively pursuing three men accused of wide-ranging and complex conspiracies of laundering stolen and illicit cryptocurrency that the North Korean regime used to finance its massive weapons programs. The Department of Justice (DoJ) this month indicted North Korean national Sim Hyon Sop, Wu HuiHui of China, and Cheng Hung Man, a Hong Kong British national, for their roles in two money laundering conspiracies, both aimed at channeling funds into North Korea's coffers. The Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK) is known for running complex operations designed to steal or generate crypto – often through state-sponsored groups – that is then laundered and sent to the regime to fund its programs around weapons of mass destruction (WMD) and ballistic missiles, which the US and other countries deem national security threats. North Korea has been operating such increasingly creative cyber schemes since at least 2017. "The charges… highlight the ways in which North Korean operatives have innovated their approach to evading sanctions by exploiting the technological features of virtual assets to facilitate payments and profits, and targeting virtual currency companies for theft," Assistant Attorney General Kenneth A Polite Jr of the DoJ's Criminal Division said in a statement. In one of the conspiracies, Wu and Cheng are accused of providing support to the notorious Lazarus Group, a group linked to numerous attacks around the world for more than a decade, targeting a variety of industries from financing and manufacturing to media, entertainment, and shipping. Google sues CryptBot slingers, gets court order to shut down malware domains https://www.theregister.com/2023/04/27/google_cryptbot_shutdown/ Google said it obtained a court order to shut down domains used to distribute CryptBot after suing the distributors of the info-stealing malware. According to the Chocolate Factory's estimates, the software nasty infected about 670,000 Windows computers in the past year, and specifically targeted Chrome users to pilfer login details, browser cookies, cryptocurrencies, and other sensitive materials from their PCs. A New York federal judge this week unsealed a lawsuit [PDF] that Google filed against the malware's slingers; the US giant accused the distributors of committing computer fraud and abuse, and trademark infringement by using Google's marks in their scam. The court granted Google a temporary restraining order, which allowed it to shut down the bot operators' internet infrastructure. Usually in this sort of case, Google gets to take its restraining order to registrars and registries that are under the court's jurisdiction, and get specific domains used to spread the malware disabled. Judging from the court order [PDF] Google can not only have domains taken down in that fashion, it can show its restraining order to network providers and hosters to get connections to the servers used by CryptBot blocked; get any of the hardware or virtual machines involved switched off and services suspended; materials that would lead to the identification of CryptBot's operators preserved and handed over; ensure steps are taken to keep this infrastructure offline; and much more. All in all, the order allows Google to wipe from the internet the systems and websites used by CryptBot's operators to spread their software nasty. "Our litigation was filed against several of CryptBot's major distributors who we believe are based in Pakistan and operate a worldwide criminal enterprise," said Google's Head of Litigation Advance Mike Trinh and its Threat Analysis Group's Pierre-Marc Bureau. The restraining order will "bolster our ongoing technical disruption efforts against the distributors and their infrastructure," they added. "This will slow new infections from occurring and decelerate the growth of CryptBot." The distributors targeted in the lawsuit – said to be Zubair Saeed, Raheel Arshad, and Mohammad Rasheed Siddiqui of Pakistan – operated websites that lured unwitting users into downloading malicious versions of Google Earth Pro and Google Chrome, we're told. Those marks thought they were getting the real deal, but instead they are fetching versions stuffed with the info-stealer malware. Once they install the software on their computers, they infect their machines with CryptBot. "Recent CryptBot versions have been designed to specifically target users of Google Chrome, which is where Google's CyberCrimes Investigations Group (CCIG) and Threat Analysis Group (TAG) teams worked to identify the distributors, investigate and take action," Trinh and Bureau said. The good, the bad and the generative AI https://www.theregister.com/2023/04/26/the_good_the_bad_and ChatGPT is just the beginning: CISOs need to prepare for the next wave of AI-powered attacks Generative AI, the result of decades of research into neural networking and Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), is widely seen as the next candidate on this list. The idea that AI is a big deal is nothing new and the generative AI that has made headlines is only one subsector of AI development. But there's no doubt that its very public arrival through chatbots such as OpenAI's ChatGPT and Google's Bard has fired a jolt of destabilizing energy into computing as a whole, and cybersecurity as a discipline. With microprocessors, you can build small computers. With the PC you can put an affordable one on everyone's desk. With the web you can connect the PC to a global information network. With the smartphone, that network can go anywhere and everywhere. What, then, will be the role for AI? The high-level answer is that it will allow automation and advanced decision making without the need to consult human beings. Humans make mistakes that machines don't. They also do things slowly and expensively. At a stroke, with generative AI many of these issues appear to vanish. Data can be processed in seconds as new insights multiply and automated decision-making accelerates. There is, of course, also a darker side to generative AI which researchers have been busily investigating since ChatGPT's public launch on the GPT-3 natural language large language model (LLM) last November. This has generated a surprising amount of doom-saying publicity for chatbots, starting with their effect on the building block of cyber-criminality, phishing emails. This author proved this by feeding ChatGPT real phishing 'security alert' emails to see how it might improve them. Not only did it correct grammatical mistakes, it added additional sections that made them sound even more authoritative. In language at least, these were impossible to distinguish from a well-composed, genuine support email written by a native speaker. Beyond simply improving the language of phishing, the obvious next step would be to make each attack more targeted. The threat here is that AI will be used to scrape data on specific people as a way of impersonating them. AI will also make it much easier for attackers to analyze the large volumes of stolen data, sifting it for sensitive topics at a speed that would be impossible today. "Learn from the environment on a continuous basis," he says. "Have machine learning that knows about the entities it is protecting and not simply the outside world." F5 Safeguards Digital Services with New AI-Powered App and API Security Capabilities https://www.f5.com/company/news/press-releases/f5-safeguards-digital-services-new-ai-powered-app-api-security How F5 Engineers are using AI to Optimize Software https://www.f5.com/company/blog/how-f5-engineers-are-using-ai-to-optimize-software1.7KViews2likes2CommentsSecure RAG for Safe AI Deployments Using F5 Distributed Cloud and NetApp ONTAP
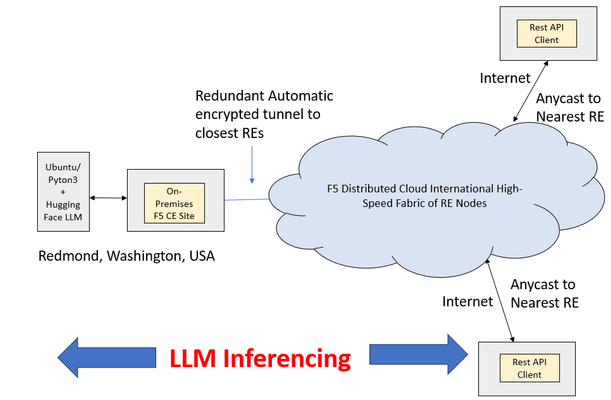
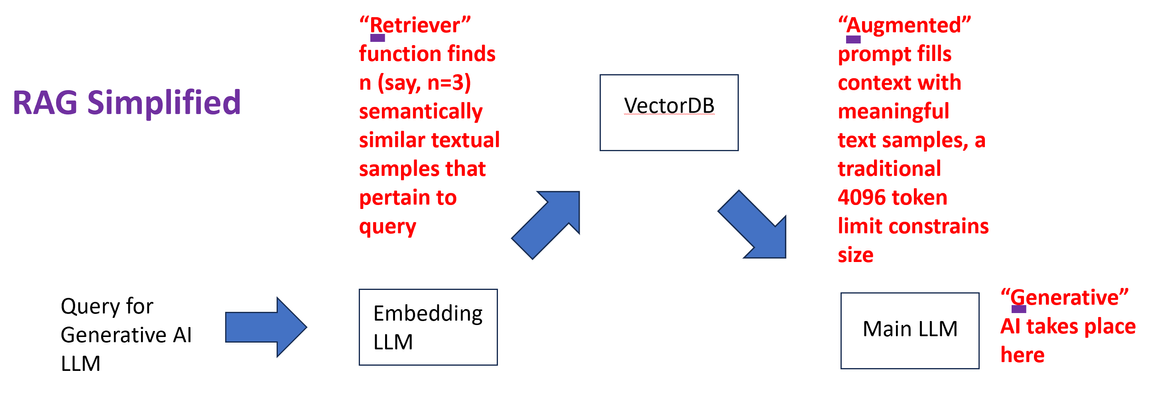
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) is one of the most discussed techniques to empower Large Language Models (LLM) to deliver niche, hyper-focused responses pertaining to specialized, sometimes proprietary, bodies of knowledge documents. Two simple examples might include highly detailed company-specific information distilled from years of financial internal reporting from financial controllers or helpdesk type queries with the LLM harvesting only relevant knowledge base (KB) articles, releases notes, and private engineering documents nor normally exposed in their entirety. RAG is highly bantered about in numerous good articles; the two principal values are: LLM responses to prompts (queries) based upon specific, niche knowledge as opposed to the general, vast pre-training generic LLMs are taught with; in fact, it is common to instruct LLMs not to answer specifically with any pre-trained knowledge. Only the content “augmenting” the prompt. Attribution is a key deliverable with RAG. Generally LLM pre-trained knowledge inquiries are difficult to traceback to a root source of truth. Prompts augmented with specific assistive knowledge normally solicit responses that clearly call out the source of the answers provided. Why is the Security of RAG Source Content Particularly Important? To maximize the efficacy of LLM solutions in the realm of artificial intelligence (AI) an often-repeated adage is “garbage in, garbage out” which succinctly states an obvious fact with RAG: valuable and actionable items must be entered into the model to expect valuable, tactical outcomes. This means exposing key forms of data, examples being data which might include patented knowledge, intellectual property not to be exposed in raw form to competitors. Actual trade secrets, which will infuse the LLM but need to remain confidential in their native form. In one example around trade secrets, the Government of Canada spells out a series of items courts will look at in determining compensation for misuse (theft) of intellectual property. It is notable that the first item listed is not the cost associated with creation of the secret material (“the cost in money or time of creating or developing the information”) but rather the very first item is instead how much effort was made to keep the content secure (“the measures taken to maintain secrecy”). With RAG, incoming queries are augmented with rich, semantically similar enterprise content. The content has already been populated into a vector database by converting documents, they might be pdf or docx as examples, into raw text form and converting chunks of text into vectors. The vectors are long sequences of numbers with similar mathematical attributes for similar content. As a trivial example, one-word chunks such as glass, cup, bucket, jar might be semantically related, meaning similarities can be construed by both human minds and LLMs. On the other hand, empathy, joy, and thoughtfulness maintain similarities of their own. This semantic approach means a phrase/sentence/paragraph (chunk) using bow to mean “to bend in respect” as opposed to the “front end of a ship” or “something to tie one’s hair back with”, even a tool every violinist would need. The list goes on; all semantic meanings of bow are very different in these chunks and would have distinctive embeddings within a vector database. The word embedding is likely derived from “fixing” or “planting” an object. In this case, words are “embedded” into a contextual understanding. The typical length of the number sequence describing the meaning of items has typically been more than 700, but this number of “dimensions” applied is always a matter of research, and the entire vector database is arrived at with an embedding LLM, distinct from the main LLM that will produce generative AI responses to our queries. Incoming queries destined for the main generative AI LLM can, in turn, be converted to vectors themselves by the very same text-embedding “helper” LLM and through retrieval (the “R” in RAG) similar textual content can buttress the prompt presented to the main LLM (double click to expand). Since a critical cog in the wheel of the RAG architecture is the ingestion of valuable and sensitive source documents into the vector database, using the embedding LLM, it is not just prudent but critical that this source content be brought securely over networks to the embedding engine. F5 Distributed Cloud Secure Multi-cloud Networking and NetApp ONTAP For many practical, time-to-market reasons, modern LLMs, both the main and embedding instances, may not be collocated with the data vaults of modern enterprises. LLMs benefit from cloud compute and GPU access, something often in short supply for on-premises production roll outs. A typical approach assisted by the economies of scale might be to harvest public cloud providers, such as Azure, AWS, and Google Cloud Platform for the compute side of AI projects. Azure, as one example, can turn up virtual machines with GPUs from NVIDIA like A100, A2, and Tesla T4 to name a few. The documents needed to feed an effective RAG solution may well be on-premises, and this is unlikely to change for reasons including governance, regulatory, and the weight of decades of sound security practice. One of the leading on-premises storage solutions of the last 25 years is the NetApp ONTAP storage appliance family, and reflected in this quote from NVIDIA: "Nearly half of the files in the world are stored on-prem on NetApp." — Jensen Huang, CEO of NVIDIA A key deliverable of F5 Distributed Cloud is providing encrypted interconnectivity of disparate physical sites and heterogeneous cloud instances such as Azure VNETs or AWS VPCs. As such, there are two immediate, concurrent F5 features that come to mind: Secure interconnectivity of on-premises NetApp volumes (NAS) or LUNs (Block) containing critical documents for ingestion into RAG. Utilize encrypted L3 connectivity between the enterprise location and the cloud instance where the LLM/RAG are instantiated. TCP load balancers are another alternative for volume sharing NAS protocols like NFS or SMB/CIFS. Secure access to the LLM web interface or RESTful API end points, with HTTPS load balancers including key features like WAF, anti-bot mechanisms, and API automatic rate limiting for abusive prompt sources. The following diagram presents the topology this article set out to create, RE are “regional edge” sites maintained internationally by F5 and harness private RE to RE, high-speed global communication links. DNS names, such as the target name of an LLM service, will leverage mappings to anycast IP addresses, thus users entering the RE network from southeast Asian might, for example, enter the Singapore RE while users in Switzerland might enter via a Paris or Frankfurt RE. Complementing the REs are Customer Edge (CE) nodes. There are virtual or physical appliances which act as security demarcation points. For instance, a CE placed in an Azure VNET can protect access to the server supporting the LLM, removing any need for Internet access to the server, which is now entirely accessible only through a private RFC-1918 type of private address. External access to the LLM for just employees or, maybe employees and contractors, or potentially access for the Internet community is enabled by a distributed HTTPS load balancer. In the example depicted above, oriented towards full Internet access, the FQDN of the LLM is projected by the load balancer into the global DNS and consumers of the service resolve the name to one IP address and are attracted to the closest RE by BGP-4’s support for anycast. As the name “distributed” load balancer suggests, the origin pool can be in an entirely different site than the incoming RE, in this case the origin pool is the LLM behind the CE in the Azure VNET. The LLM requests travel from RE to CE via a highspeed networking underlay. The portion of the solution that securely ties the LLM to the source content required for RAG to embed vectors, is in this case, utilizing layer 3 multi-cloud networking (MCN). The solution is turnkey, routing table are automatically connected to members of the L3 MCN, in this case the inside interfaces of the Azure CE and Redmond, Washington on-premises CE and traffic flows over an encrypted underlay network. As such, the NetApp ONTAP cluster can securely expose volumes with key file ware via a protocol like Network File System (NFS), no risk of data exposure to third-party prying eyes exists. The following diagram drills into the RE and CE and NetApp interplay (double click to expand). F5 Distributed Cloud App Connect and LLM Setup This article speaks to hands-on experience with web-driven LLM inferencing with augmented prompts derived from a RAG implementation. The AI compute was instantiated on an Azure-hosted Ubuntu 20.04 virtual machine with 4 virtual cores. Installed software included Python 3.10, and libraries such as Langchain, Pypdf (for converting pdf documents to text), FAISS (for similarity searching via a vector database), and other libraries. The actual open source LLM utilized for the generative AI is found here on huggingface.co. The binary exceeds 4 GB however, is considered effective for CPU-based deployments. The embedding LLM model, critical to seed the vector database with entries derived from secured enterprise documentation, and then used again per incoming query for RAG similarity searches to build augmented prompts, was from Hugging Face: sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2 and can be found here. The AI RAG solution was implemented in Python3, and as such the Azure Ubuntu can be accessed both by SSH or via Jupyter Notebooks. The latter was utilized as this is the preferred final delivery mechanism for standard users, not a web chatbot design or the requirement to use API commands through solutions like Postman or Curl. This design choice, to steer the user experience towards Jupyter Notebook consumption, is in keeping with the fact that it has become a standard in AI LLM usage where the LLM is tactical and vital to an enterprise's lines of business (LOBs). Jupyter Notebooks are web-accessed with a browser like Chrome or Edge and as such, F5’s WAF, anti-bot, and L7 DDoS, all part of the F5 WAAP offering, can easily be laid upon an HTTP load balancer with a few mouse clicks in XC to provide premium security to the user experience. NetApp and F5 Distributed Cloud Secure Multi-cloud Networking The secure access to files for ingestion into the vector database, for similarity searches when user queries are received, makes use of an encrypted L3 Multi-cloud Network relationship between the Azure VNET and the LAN on prem in Redmond, Washington hosting the NetApp ONTAP cluster. The specific protocol chosen was NFS and the simplicity is demonstrated by the use of one Linux command to present key, high-valued documents for the AI steps to populate the database: #mount -t nfs <IP Address of NetAPP LIF interface on-prem>:/Secure_docs_for_RAG /home/ubuntu_restriced_user/rag_project/docs/Secure_docs_for_RAG. This address is available nowhere else in the world except behind this F5 CE in the Azure VNET. After the pdf files are converted to text, chunked to reasonable sizes with some overlap suggested between the end of one chunk and the start of the next chunk, the embedding LLM will populate the vector database. The files are always only accessed remotely by NFS through the mounted volume, and this mount may be terminated until new documents are ready to be added to the solution. The Objective RAG Implementation - Described In order to have a reasonable facsimile of the real-word use cases this solution will empower today, but not having any sensitive documents to be injected, it was decided to use some seminal “Internet Boom”-era IETF Requests for Comment (RFCs) as source content. With the rise of multi-port routing and switching devices, it became apparent the industry badly needed specific and highly precise definitions around network device (router and switch) performance benchmarking to allow purchasers “apples-to-apples” comparisons. These documents recommend testing parameters, such as what frame or packet sizes to test with, test iteration time lengths, when to use FIFO vs LIFO vs LILO definitions of latency, etc. RFC-1242 (Request for Comment, terminology) and RFC-2544 (methodologies), chaired by Scott Bradner of Harvard University, and the later RFC 2285 (LAN switching terminologies), chaired by Bob Mandeville then of European Network Laboratories are three prominent examples, to which test and measurement solutions aspired to be compliant. Detailed LLM answers for quality assurance engineers in the network equipment manufacturing (NEM) space is the intended use case of the design, answers that must be distilled specifically by generative AI considering queries augmented by RAG and specifically only based upon these industry-approved documents. These documents are, of course, not containing trade secrets or patented engineering designs. They are in fact publicly available from the IETF, however they are nicely representative of the value offered in sensitive environments. Validating RAG – Watching the Context Provided to the LLM To ensure RAG was working, the content being augmented in the prompt was displayed to screen, we would expect to see relevant clauses and sentences from the RFCs being provided to the generative AI LLM. Also, if we were to start by asking questions that were outside the purview of this testing/benchmarking topic, we should see the LLM struggle to provide users a meaningful answer. To achieve this, rather than, say, asking what 802.3/Ethernetv2 frame sizes should be used in throughput measurements, and what precisely is the industry standard definition of the term “throughput” was, the question instead pertained to a recent Netflix release, featuring Lindsay Lohan. Due to the recency of the film, even if the LLM leaned upon its pretrained model, it will come up with nothing meaningful. “Question: Important, only use information provided as context in the prompt, do not use other trained knowledge. Please identify who played Heather in the March 2024 Lindsay Lohan Netflix movie titled Irish Wish?” As seen in the following Jupyter screenshot, the RAG solution can only provide augmented prompts from the database, in this case it has some test and measurement clauses and some rules pertaining to the winter ice sport of curling (double click to enlarge). The supportive context data augmenting the prompt was, as expected, not going to help in this off-the-wall query, as only the RFCs and some sports rules had been introduced to the vector database. What is especially noteworthy is the LLM did not simply admit it could not possibly answer this question but hallucinated a very articulate response that indicated “Heather played for her team against Lindsay Lohan’s Team Ireland”. To validate the RAG architecture for a working scenario, actually pertinent to the movie, a film review in pdf format was added to the ONTAP cluster-housed volume. The supportive documentation was consumed (using Pypdf from the Jupyter Notebook it became text). It was automatically chunked and introduced to the FAISS vector database through the Hugging Face embedding LLM. With the RAG vector database populated by the embedding LLM, the responses then became meaningful. The following exchange shows the value of RAG in producing meaningful, thought-out answers: Question: Important, only use information provided as context in the prompt, do not use other pre-trained knowledge. Who does Maddie edit novels for in the Lindsay Lohan March 2024 Netflix movie titled Irish Wish? Answer: Let's think step by step. We know that Maddie Kelly plays a book editor who harbors a big secret, and we have been given information about her job as an editor for Paul Kennedy (played by Alexander Vlahos), which is also part of the question context provided above. Therefore it seems logical to infer that she edits novels in general but specifically those written or co-written by author Paul Kennedy - who happens to be a bestselling romance novelist as stated earlier on, so we can safely conclude Maddie works for Paul himself (as opposed to any other book publishing company). This time we see relevant, meaningful context provided by RAG, with relevant portions of the pdf file review document augmenting the prompt. The augmentations are normally not displayed unless requested by the user or programmer, unlike humans, LLMs do not require superfluous text formatting (advantage: LLMs) and thus the content is packed tightly and efficiently. Fewer characters also mean fewer tokens get used by the targeted AI model and can allow more data before a token context limit is reached. In pay-for-use LLM approaches fewer tokens also help the enterprise’s bottom line financially. Also, note that the answer will likely not always be identical with subsequent asks of the same question as per LLM normal behavior. Features like “temperature setting” can also allow more “creative” ideas in responses, injecting humor and even outlandishness if desired. The RAG workflow is now validated, but the LLMs in question (embedding and main generative LLM) can still be made better with these suggestions: Increase “chunk” sizes so ideas are not lost when excessive breaks make for short chunks. Increase “overlap” so an idea/concept is not lost at the demarcation point of two chunks. Most importantly, provide more context from the vector database as context lengths (maximum tokens in a request/response) are generally increasing in size. Llama2, for instance, typically has a 4,096 context length but can now be used with larger values, such as 32,768. This article used only 3 augmentations to the user query, better results could be attained by increasing this value at a potential cost of more CPU cycles. Using Secure RAG – F5 L3 MCN, HTTPS Load Balancers and NetApp ONTAP Together With the RAG architecture validated to be working, the solution was used to assist the target user entering queries to the Azure server by means of Jupyter Notebooks, with RAG documents ingested over encrypted, private networking to the on-premises ONTAP cluster NFS volumes. The questions posed, which are answerable by reading and understanding key portions spread throughout the Scott Bradner RFCs, was: “Important, only use information provided as context in the prompt, do not use other pre-trained knowledge. Please explain the specific definition of throughput? What 802.3 frame sizes should be used for benchmarking? How long should each test iteration last? If you cannot answer the questions exclusively with the details included in the prompt, simply say you are unable to answer the question accurately. Thank you." The Jupyter Notebook representation of this query, which is made in the Python language and issued from the user’s local browser anywhere in the world and directly against the Azure-hosted LLM, looks like the following (click to expand image): The next screenshot demonstrates the result, based upon the provided secure documents (double click to expand). The response is decent, however, the fact that it is clearly using the provided augmentations to the prompt, that is the key objective of this article. The accuracy of the response can be questionable in some areas, the Bradner RFCs highlighted the importance of 64-byte 802.3/Ethernetv2 frame sizes in testing, as line rate forwarding with this minimum size produces the highest theoretically possible frame per second load. In the era of software driven forwarding in switches and routers this was very demanding. Sixty-four byte frames result in 14,881 fps (frames per second) for 10BaseT, 148,809 fps for 100BaseT, 1.48 million fps for Gigabit Ethernet. These values were frequently more aspirational in earlier times and also a frequent metric used in network equipment purchasing cycles. Suspiciously, the LLM response calls out 64kB in 802.3 testing, not 64B, something which seems to be an error. Again, with this architecture, the actual LLM providing the generative AI responses is increasingly viewed as a commodity, alternative LLMs can be plugged quickly and easily into the RAG approach of this Jupyter Notebook. The end user, and thus the enterprise itself, is empowered to utilize both different LLMs, purchased or open-source from sites like Hugging Face, to determine optimal results. The other key change that can affect the overall accuracy of results is to experiment with different embedding models. In fact, there are on-line “leader” boards strictly for embedding LLMs so one can quickly swap in and out various popular embedding LLMs to see the impact on results. Summary and Conclusions on F5 and NetApp as Enablers for Secure RAG This article demonstrated an approach to AI usage that leveraged the compute and GPU availability that can be found today within cloud providers such as Azure. To safely access such an AI platform for a production-grade enterprise requirement, F5 Distributed Cloud (XC) provided HTTPS load balancers to connect worker browsers to a Jupyter Notebook service on the AI platform, this service applies advanced security upon the traffic within the XC, from WAF to anti-bot to L3/L7 DDOS protections. Utilizing secure Multi-cloud Networking (MCN), F5 provided a private L3 connectivity service between the inside interface on an Azure VNET-based CE (customer edge) node and the inside interface of an on-premises CE node in a building in Redmond, Washington. This secure network facilitated a NFS remote volume, content on spindles/flash in on-premises NetApp ONTAP to be remotely mounted on the Azure server. This secure file access provided peace of mind to exposing potentially critical and private materials from NetApp ONTAP volumes to the AI offering. RAG was configured and files were ingested, populating a vector database within the Azure server, that allowed details, ideas, and recommendations to be harnessed by a generative AI LLM by augmenting user prompts with text gleaned from the vector database. Simple examples were used to first demonstrate that RAG was working by posing queries that should not have been addressed by the loaded secure content; such a query was not suitably answered as expected. The feeding of meaningful content from ONTAP was then demonstrated to unleash the potential of AI to address queries based upon meaningful .pdf files. Opportunities to improve results by swapping in and out the main generative AI model, as well as the embedding model, were also considered.371Views1like0CommentsHow AI Will Automate Cybersecurity in the Post-COVID World
Widespread remote working is accelerating the trend of digitization in society and a derivative trend of this acceleration is our increased reliance on online applications - which also means cybercrime is becoming more lucrative. Over on F5 Labs, Shuman Ghosemajumder briefly introduces the problem space and links to an article on VentureBeat about how AI will Automate cybersecurity in a Post-Covid world. https://www.f5.com/labs/articles/bylines/how-ai-will-automate-cybersecurity-in-the-post-covid-world232Views1like0Comments